Materials in practice
In this section we will analyze how to set up the various material parameters in Blender, and what you should expect as a result.
Once an Object is selected by pressing the F5 key or
 the material buttons window appears (Figure 4).
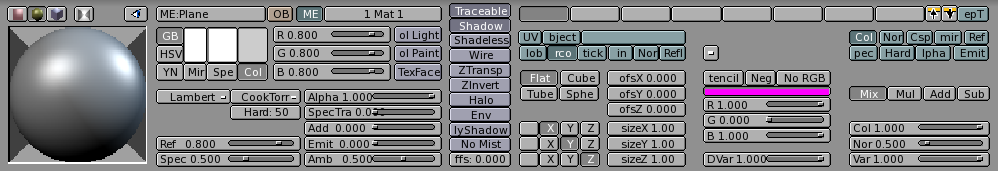
Of these buttons, the left block (Figure 5) is
strictly relevant to material shaders, while the right block is relevant to material
textures and will be analyzed in the pertinent section.
the material buttons window appears (Figure 4).
Of these buttons, the left block (Figure 5) is
strictly relevant to material shaders, while the right block is relevant to material
textures and will be analyzed in the pertinent section.
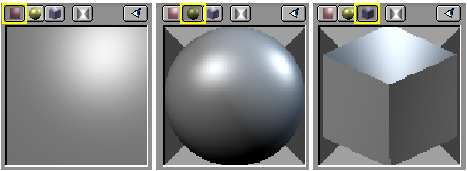
In this block the leftmost sub-block presents the material preview. By default it is a plane seen from the top, but it can be set to a sphere or to a cube with the buttons on top of the preview window (Figure 6).
Material Colours
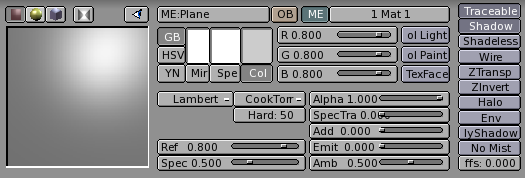
The next group of buttons (Figure 7) determines the material colours.
Each material can exhibit up to three colours:
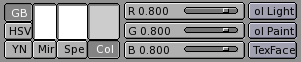
The basic material colour, or the Diffuse colour, or, briefly the Color tout court (Col button in the interface) which is the colour used by the diffuse shader.
The Specular colour, indicated by the Spe button in the interface, is the colour used by the specular shader.
The Mirror colour, indicated by the Mir button in the interface, is the colour used by special textures to fake mirror reflections. More information on this will be given in the Environment Mapping section.
The aforementioned buttons select the pertinent colour, which is shown in preview immediately above the button. The three sliders on the right allow you to change the values for the colour both in a RGB scheme and in a HSV scheme. You can select these schemes via the RGB and HSV buttons on the far left.
The DYN button is used to set the Dynamic properties of the Object in the RealTime engine, which is outside the scope of this manual, while the three buttons on the far right are relative to advanced Vertex Paint and UV Texture.
The Shaders
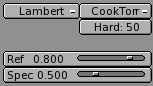
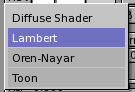
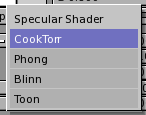
Underneath the colour buttons there are the shader buttons (Figure 8). On the top, the two pop-up menus allow you to select one diffuse shader (on the right, Figure 9) and one specular shader (on the left, Figure 10).
Below these there are two sliders, valid for all shaders, determining the intensity of the Diffusion and Specular phenomena. The Ref slider has a 0 to 1 range whereas the Spec has a 0 to 2 range. Strictly Physically speaking, if A is the light energy impinging on the object, then Ref times A is the energy diffused and Spec times A is the energy specularly reflected and, to be physically correct it must be Ref + Spec < 1 or the object would radiate more energy that it receives.
But this is CG, so don't be too strict on physics.